Introduction to Bioconductor Classes
Lori Shepherd Kern Lori.Shepherd@roswellpark.org
Source:vignettes/day_4.Rmd
day_4.RmdIntroduction
Common Bioconductor Classes
| Data Type | Package Name | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Rectangular feature x sample data (RNAseq count matrix, microarray, …) | SummarizedExperiment | SummarizedExperiment() |
| Genomic coordinates (1-based, closed interval) | GenomicRanges | GRanges() or GRangesList() |
| Ragged genomic coordinates | RaggedExperiment | RaggedExperiment() |
| DNA / RNA / AA sequences | Biostrings | *StringSet() |
| Gene sets | BiocSet GSEABase |
BiocSet() GeneSet() or GeneSetCollection() |
| Multi-omics data | MultiAssayExperiment | MultiAssayExperiment() |
| Single cell data | SingleCellExperiment | SingleCellExperiment() |
| Mass spec data | Spectra | Spectra() |
| File formats | BiocIO | BiocFile-class |
Three Commonly Used or Extended Classes
Biostrings::*StringSets
GenomicRanges::GenomicRanges
SummarizedExperiment::SummarizedExperiment
Genomic Sequences
- Valid data, e.g., alphabet
- ‘Vector’ interface:
length(),[, … - Specialized operations, e.g,.
reverseComplement()
Classes
- BString / BStringSet
- DNAString / DNAStringSet
- RNAString / RNAStringSet
- AAString / AAStringSet
DNA Sequence Example
library(Biostrings)
dna <- DNAStringSet(c("AAACTG", "CCCTTCAAC", "TACGAA"))
dna## DNAStringSet object of length 3:
## width seq
## [1] 6 AAACTG
## [2] 9 CCCTTCAAC
## [3] 6 TACGAA
length(dna)## [1] 3
dna[c(1, 3, 1)]## DNAStringSet object of length 3:
## width seq
## [1] 6 AAACTG
## [2] 6 TACGAA
## [3] 6 AAACTGDNA Sequence Example cont.
width(dna)## [1] 6 9 6
as.character(dna[c(1,2)])## [1] "AAACTG" "CCCTTCAAC"
reverseComplement(dna)## DNAStringSet object of length 3:
## width seq
## [1] 6 CAGTTT
## [2] 9 GTTGAAGGG
## [3] 6 TTCGTA
Importing Genomic Sequence
Import Methods from FASTA/FASTQ
- readBStringSet / readDNAStringSet / readRNAStringSet / readAAStringSet
filepath1 <- system.file("extdata", "someORF.fa", package="Biostrings")
x1 <- readDNAStringSet(filepath1)
x1## DNAStringSet object of length 7:
## width seq names
## [1] 5573 ACTTGTAAATATATCTTTTATTT...CTTATCGACCTTATTGTTGATAT YAL001C TFC3 SGDI...
## [2] 5825 TTCCAAGGCCGATGAATTCGACT...AGTAAATTTTTTTCTATTCTCTT YAL002W VPS8 SGDI...
## [3] 2987 CTTCATGTCAGCCTGCACTTCTG...TGGTACTCATGTAGCTGCCTCAT YAL003W EFB1 SGDI...
## [4] 3929 CACTCATATCGGGGGTCTTACTT...TGTCCCGAAACACGAAAAAGTAC YAL005C SSA1 SGDI...
## [5] 2648 AGAGAAAGAGTTTCACTTCTTGA...ATATAATTTATGTGTGAACATAG YAL007C ERP2 SGDI...
## [6] 2597 GTGTCCGGGCCTCGCAGGCGTTC...AAGTTTTGGCAGAATGTACTTTT YAL008W FUN14 SGD...
## [7] 2780 CAAGATAATGTCAAAGTTAGTGG...GCTAAGGAAGAAAAAAAAATCAC YAL009W SPO7 SGDI...Importing Genomic Sequences
Utilizing BSgenome Packages
BSgenome packages contain sequence information for a given species/build. There are many such packages - you can get a listing using BiocManager::available("BSgenome")
## 'getOption("repos")' replaces Bioconductor standard repositories, see
## 'help("repositories", package = "BiocManager")' for details.
## Replacement repositories:
## CRAN: https://cloud.r-project.org## [1] "BSgenome"
## [2] "BSgenome.Alyrata.JGI.v1"
## [3] "BSgenome.Amellifera.BeeBase.assembly4"
## [4] "BSgenome.Amellifera.NCBI.AmelHAv3.1"
## [5] "BSgenome.Amellifera.UCSC.apiMel2"
## [6] "BSgenome.Amellifera.UCSC.apiMel2.masked"Can’t find what you are looking for? Check out the new BSgenomeForge for creating a BSgenome package.
BSgenome
We can load and inspect a BSgenome package
library(BSgenome.Hsapiens.UCSC.hg19)
BSgenome.Hsapiens.UCSC.hg19## | BSgenome object for Human
## | - organism: Homo sapiens
## | - provider: UCSC
## | - genome: hg19
## | - release date: June 2013
## | - 298 sequence(s):
## | chr1 chr2 chr3
## | chr4 chr5 chr6
## | chr7 chr8 chr9
## | chr10 chr11 chr12
## | chr13 chr14 chr15
## | ... ... ...
## | chr19_gl949749_alt chr19_gl949750_alt chr19_gl949751_alt
## | chr19_gl949752_alt chr19_gl949753_alt chr20_gl383577_alt
## | chr21_gl383578_alt chr21_gl383579_alt chr21_gl383580_alt
## | chr21_gl383581_alt chr22_gl383582_alt chr22_gl383583_alt
## | chr22_kb663609_alt
## |
## | Tips: call 'seqnames()' on the object to get all the sequence names, call
## | 'seqinfo()' to get the full sequence info, use the '$' or '[[' operator to
## | access a given sequence, see '?BSgenome' for more information.Subsetting a BSgenome
The main accessor is getSeq, and you can get data by sequence (e.g., entire chromosome or unplaced scaffold), or by passing in a GRanges object, to get just a region.
getSeq(BSgenome.Hsapiens.UCSC.hg19, "chr1")## 249250621-letter DNAString object
## seq: NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN...NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN## DNAStringSet object of length 1:
## width seq
## [1] 85634 GCGGAGCGTGTGACGCTGCGGCCGCCGCGGACCT...AATGGGAATTAAATATTTAAGAGCTGACTGGAAGenomic Ranges
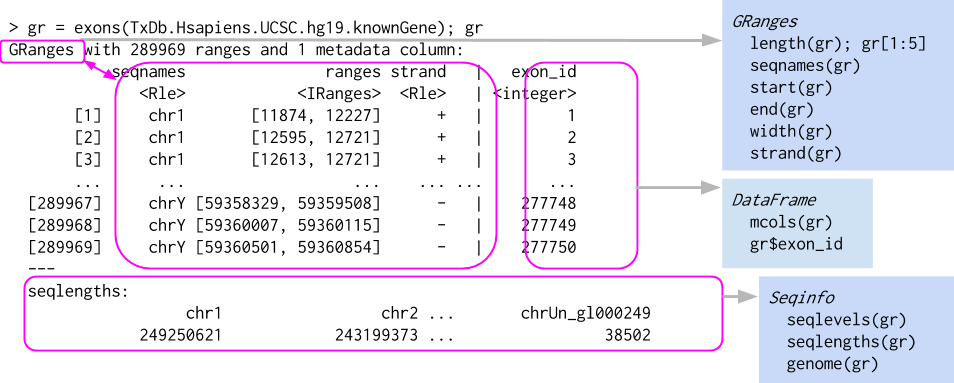
GenomicRanges objects allow for easy selection and subsection of data based on genomic position information.
Where are GenomicRanges used?
Everywhere…
- Data (e.g., aligned reads, called peaks, copy number)
- Annotations (e.g., genes, exons, transcripts, TxDb)
- Close relation to BED files (see
rtracklayer::import.bed()and HelloRanges) - Anywhere there is Genomic positioning information
Utility
GenomicRanges
library(GenomicRanges)
gr <- GRanges(c("chr1:100-120", "chr1:115-130"))
gr## GRanges object with 2 ranges and 0 metadata columns:
## seqnames ranges strand
## <Rle> <IRanges> <Rle>
## [1] chr1 100-120 *
## [2] chr1 115-130 *
## -------
## seqinfo: 1 sequence from an unspecified genome; no seqlengths
gr <- GRanges(c("chr1:100-120", "chr1:115-130", "chr2:200-220"),
strand=c("+","+","-"), GC = seq(1, 0, length=3), id = paste0("id",1:3))
gr## GRanges object with 3 ranges and 2 metadata columns:
## seqnames ranges strand | GC id
## <Rle> <IRanges> <Rle> | <numeric> <character>
## [1] chr1 100-120 + | 1.0 id1
## [2] chr1 115-130 + | 0.5 id2
## [3] chr2 200-220 - | 0.0 id3
## -------
## seqinfo: 2 sequences from an unspecified genome; no seqlengthsThere are lots of utility functions for GRange objects
Help!
GRanges functions
Intra-range operations
Inter-range operations
- e.g.,
reduce(),coverage(),gaps(),disjoin()
Between-range operations

GRanges Example
shift(gr, 1)## GRanges object with 3 ranges and 2 metadata columns:
## seqnames ranges strand | GC id
## <Rle> <IRanges> <Rle> | <numeric> <character>
## [1] chr1 101-121 + | 1.0 id1
## [2] chr1 116-131 + | 0.5 id2
## [3] chr2 201-221 - | 0.0 id3
## -------
## seqinfo: 2 sequences from an unspecified genome; no seqlengths
reduce(gr)## GRanges object with 2 ranges and 0 metadata columns:
## seqnames ranges strand
## <Rle> <IRanges> <Rle>
## [1] chr1 100-130 +
## [2] chr2 200-220 -
## -------
## seqinfo: 2 sequences from an unspecified genome; no seqlengths
anno <- GRanges(c("chr1:110-150", "chr2:150-210"))
countOverlaps(anno, gr)## [1] 2 1More examples
Returning to BSGenome: Get the sequences for three UTR regions? threeUTRsByTranscript() returns a GRangesList
library(TxDb.Hsapiens.UCSC.hg19.knownGene)
txdb <- TxDb.Hsapiens.UCSC.hg19.knownGene
threeUTR <- threeUTRsByTranscript(txdb, use.names=TRUE)
threeUTR_seq <- extractTranscriptSeqs(Hsapiens, threeUTR)
options(showHeadLines = 3, showTailLines = 2)
threeUTR_seq## DNAStringSet object of length 60740:
## width seq names
## [1] 770 TGCCCGTTGGAGAAAACAGGG...AAAGCACACTGTTGGTTTCTG uc010nxq.1
## [2] 1333 CTGTGAGGCCATTTCCAGGCC...GCCCCTCCCACGCGGACAGAG uc009vjk.2
## [3] 2976 CTGTGAGGCCATTTCCAGGCC...AATGAAAAATATCGCCCACGA uc001aau.3
## ... ... ...
## [60739] 1191 GCACCCTGACCCTATTCAGCA...TATGGAATTTGTATTTAATAA uc011mgh.2
## [60740] 1191 GCACCCTGACCCTATTCAGCA...TATGGAATTTGTATTTAATAA uc011mgi.2More examples
How many genes are between 2858473 and 3271812 on chr2 in the hg19 genome?
gns <- genes(txdb)## 403 genes were dropped because they have exons located on both strands of the
## same reference sequence or on more than one reference sequence, so cannot be
## represented by a single genomic range.
## Use 'single.strand.genes.only=FALSE' to get all the genes in a GRangesList
## object, or use suppressMessages() to suppress this message.## GRanges object with 1 range and 1 metadata column:
## seqnames ranges strand | gene_id
## <Rle> <IRanges> <Rle> | <character>
## 7260 chr2 3192741-3381653 - | 7260
## -------
## seqinfo: 93 sequences (1 circular) from hg19 genome
## OR
subsetByOverlaps(gns, GRanges("chr2:2858473-3271812"))## GRanges object with 1 range and 1 metadata column:
## seqnames ranges strand | gene_id
## <Rle> <IRanges> <Rle> | <character>
## 7260 chr2 3192741-3381653 - | 7260
## -------
## seqinfo: 93 sequences (1 circular) from hg19 genomeImporting a BED file
We said earlier, GRanges are closely related to bed files. Lets look at the example in the rtracklayer::import.bed help page:
library(rtracklayer)
test_bed <- system.file(package = "rtracklayer", "tests", "test.bed")
test <- import(test_bed)
test## UCSC track 'ItemRGBDemo'
## UCSCData object with 5 ranges and 5 metadata columns:
## seqnames ranges strand | name score itemRgb
## <Rle> <IRanges> <Rle> | <character> <numeric> <character>
## [1] chr7 127471197-127472363 + | Pos1 0 #FF0000
## [2] chr7 127472364-127473530 + | Pos2 2 #FF0000
## [3] chr7 127473531-127474697 - | Neg1 0 #FF0000
## [4] chr9 127474698-127475864 + | Pos3 5 #FF0000
## [5] chr9 127475865-127477031 - | Neg2 5 #0000FF
## thick blocks
## <IRanges> <IRangesList>
## [1] 127471197-127472363 1-300,501-700,1068-1167
## [2] 127472364-127473530 1-250,668-1167
## [3] 127473531-127474697 1-1167
## [4] 127474698-127475864 1-1167
## [5] 127475865-127477031 1-1167
## -------
## seqinfo: 2 sequences from an unspecified genome; no seqlengthsBed file continued
In fact this class Extends the GenomicRange GRange class
is(test, "GRanges")## [1] TRUESo you can use GRange functions
subsetByOverlaps(test, GRanges("chr7:127471197-127472368"))## UCSC track 'ItemRGBDemo'
## UCSCData object with 2 ranges and 5 metadata columns:
## seqnames ranges strand | name score itemRgb
## <Rle> <IRanges> <Rle> | <character> <numeric> <character>
## [1] chr7 127471197-127472363 + | Pos1 0 #FF0000
## [2] chr7 127472364-127473530 + | Pos2 2 #FF0000
## thick blocks
## <IRanges> <IRangesList>
## [1] 127471197-127472363 1-300,501-700,1068-1167
## [2] 127472364-127473530 1-250,668-1167
## -------
## seqinfo: 2 sequences from an unspecified genome; no seqlengthsSide Note:
Utilizing Bioconductor recommended import/export methods, classes, etc. has other benefits as well…
BED files have 0-based half-open intervals (left end point included, right endpoint ‘after’ the end of the range),
whereas in other parts of the bioinformatic community and in bioc the coordinates are 1-based and closed
Using import() converts BED coordinates into bioc coordinates.
Working with BAM files
library(GenomicAlignments)
fls <- list.files(system.file("extdata", package="GenomicAlignments"),
recursive=TRUE, pattern="*bam$", full=TRUE)
names(fls) <- basename(fls)
bf <- BamFileList(fls, index=character(), yieldSize=1000)
genes <- GRanges(
seqnames = rep(c("chr2L", "chr2R", "chr3L"), c(4, 5, 2)),
ranges = IRanges(c(1000, 3000, 4000, 7000, 2000, 3000, 3600,
4000, 7500, 5000, 5400),
width=c(rep(500, 3), 600, 900, 500, 300, 900,
300, 500, 500)))
se <- summarizeOverlaps(genes, bf)
se## class: RangedSummarizedExperiment
## dim: 11 2
## metadata(0):
## assays(1): counts
## rownames: NULL
## rowData names(0):
## colnames(2): sm_treated1.bam sm_untreated1.bam
## colData names(0):
# Start differential expression analysis with the DESeq2 or edgeRSummarized Experiments
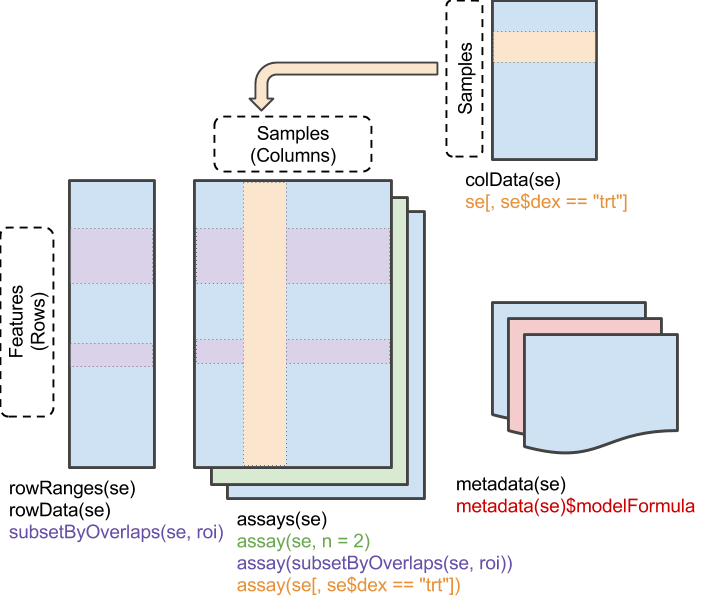
SummarizedExperiment objects are popular objects for representing expression data and other rectangular data (feature x sample data). Incoming packages are now strongly recommended to use this class representation instead of ExpressionSet.
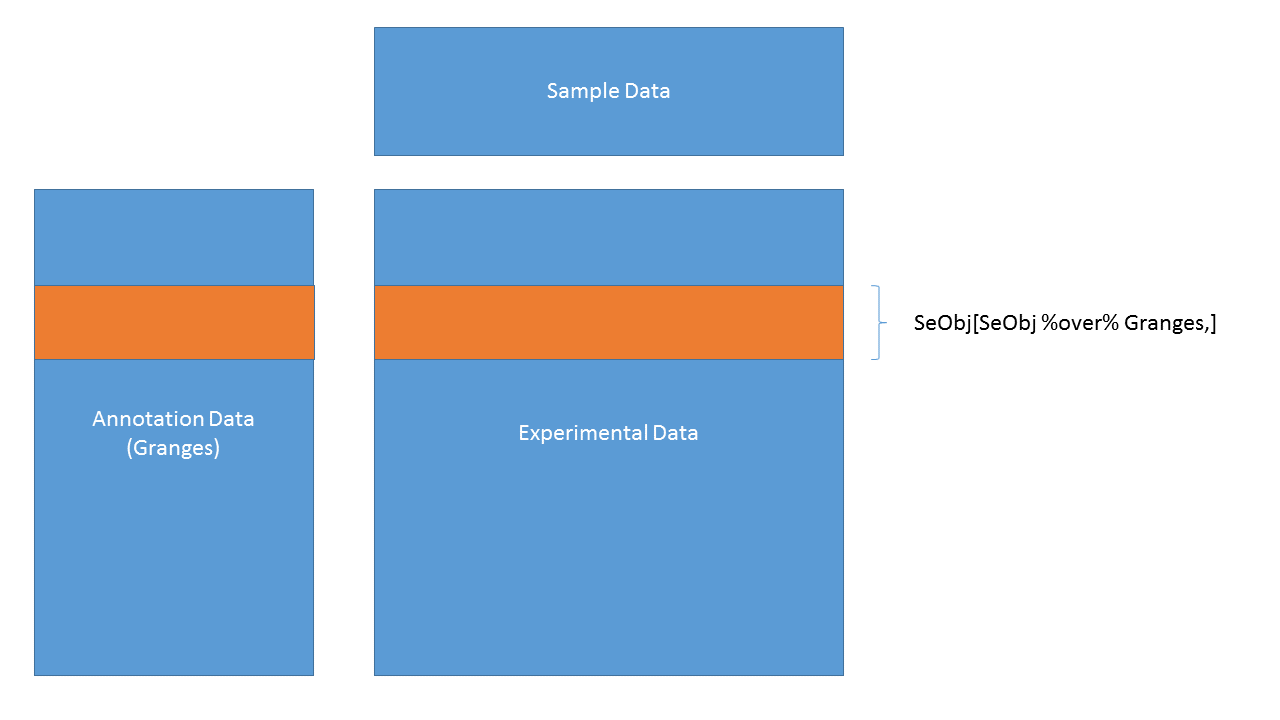
three components: underlying ‘matrix’ ‘row’ annotations (genomic features) ‘column’ annotations (sample descriptions)
Components 1.
Main matrix of values / count data / expression values / etc …
countsFile <- system.file(package = "RPG520", "extdata", "airway_counts.csv")
counts <- as.matrix(read.csv(countsFile, row.names=1))
head(counts, 3)## SRR1039508 SRR1039509 SRR1039512 SRR1039513 SRR1039516
## ENSG00000000003 679 448 873 408 1138
## ENSG00000000419 467 515 621 365 587
## ENSG00000000457 260 211 263 164 245
## SRR1039517 SRR1039520 SRR1039521
## ENSG00000000003 1047 770 572
## ENSG00000000419 799 417 508
## ENSG00000000457 331 233 229Component 2.
Sample data / Phenotypic data / Sample specific information / etc …
colDataFile <- system.file(package = "RPG520", "extdata", "airway_colData.csv")
colData <- read.csv(colDataFile, row.names=1)
colData[, 1:4]## SampleName cell dex albut
## SRR1039508 GSM1275862 N61311 untrt untrt
## SRR1039509 GSM1275863 N61311 trt untrt
## SRR1039512 GSM1275866 N052611 untrt untrt
## SRR1039513 GSM1275867 N052611 trt untrt
## SRR1039516 GSM1275870 N080611 untrt untrt
## SRR1039517 GSM1275871 N080611 trt untrt
## SRR1039520 GSM1275874 N061011 untrt untrt
## SRR1039521 GSM1275875 N061011 trt untrtComponent 3.
Genomic position information / Information about features / etc …
rangesFile <- system.file(package = "RPG520", "extdata", "airway_rowRanges.rds")
rowRanges <- updateObject(readRDS(rangesFile))
options(showHeadLines = 3, showTailLines = 2)
rowRanges## GRangesList object of length 33469:
## $ENSG00000000003
## GRanges object with 17 ranges and 2 metadata columns:
## seqnames ranges strand | exon_id exon_name
## <Rle> <IRanges> <Rle> | <integer> <character>
## [1] X 99883667-99884983 - | 667145 ENSE00001459322
## [2] X 99885756-99885863 - | 667146 ENSE00000868868
## [3] X 99887482-99887565 - | 667147 ENSE00000401072
## ... ... ... ... . ... ...
## [16] X 99891790-99892101 - | 667160 ENSE00001863395
## [17] X 99894942-99894988 - | 667161 ENSE00001828996
## -------
## seqinfo: 722 sequences (1 circular) from an unspecified genome
##
## ...
## <33468 more elements>Benefit of Containers
Could manipulate independently…
cidx <- colData$dex == "trt"
plot(
rowMeans(1 + counts[, cidx]) ~ rowMeans(1 + counts[, !cidx]),
log="xy"
)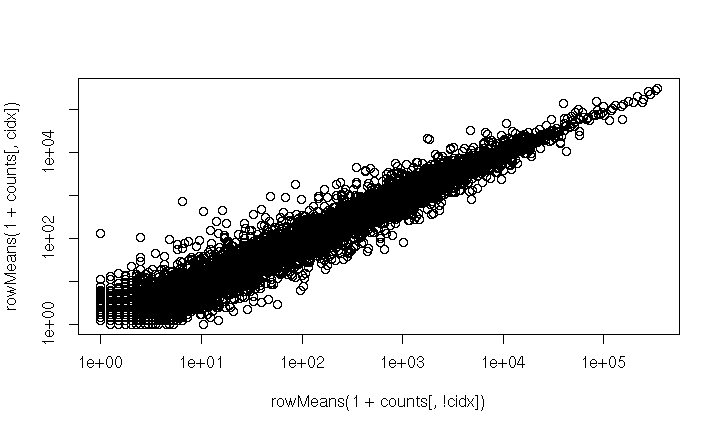
- very fragile, e.g., what if
colDatarows had been re-ordered?
SummarizedExperiment
Solution: coordinate in a single object – SummarizedExperiment
library(SummarizedExperiment)
se <- SummarizedExperiment(counts, rowRanges = rowRanges, colData = colData)
cidx <- se$dex == "trt"
plot(
rowMeans(1 + assay(se)[, cidx]) ~ rowMeans(1 + assay(se)[, !cidx]),
log="xy"
)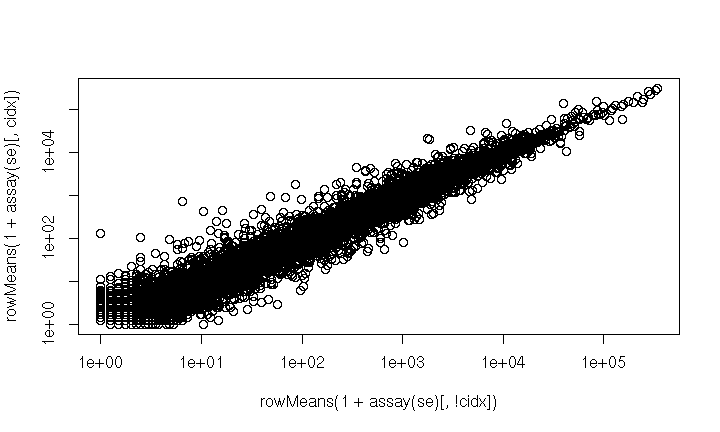
Benefits
- Much more robust to ‘bookkeeping’ errors
- matrix-like interface:
dim(), two-dimensional[, … - accessors:
assay(),rowData()/rowRanges(),colData(), …
dim(se)## [1] 33469 8
colnames(se[1:2,3:4])## [1] "SRR1039512" "SRR1039513"
names(colData)## [1] "SampleName" "cell" "dex" "albut" "Run"
## [6] "avgLength" "Experiment" "Sample" "BioSample"Popular
Many package make use of or extend the ideas of SummarizedExperiment
- SingleCellExpeirment
- TimeSeriesExperiment
- LoomExperiment
- TreeSummarizedExperiment
- MultiAssayExperiment



Help
In R:
methods(class="SummarizedExperiment")
?"SummarizedExperiment"
browseVignettes(package="SummarizedExperiment")- Support site, https://support.bioconductor.org
- Bioc-devel, bioc-devel@r-project.org
Website: https://bioconductor.org

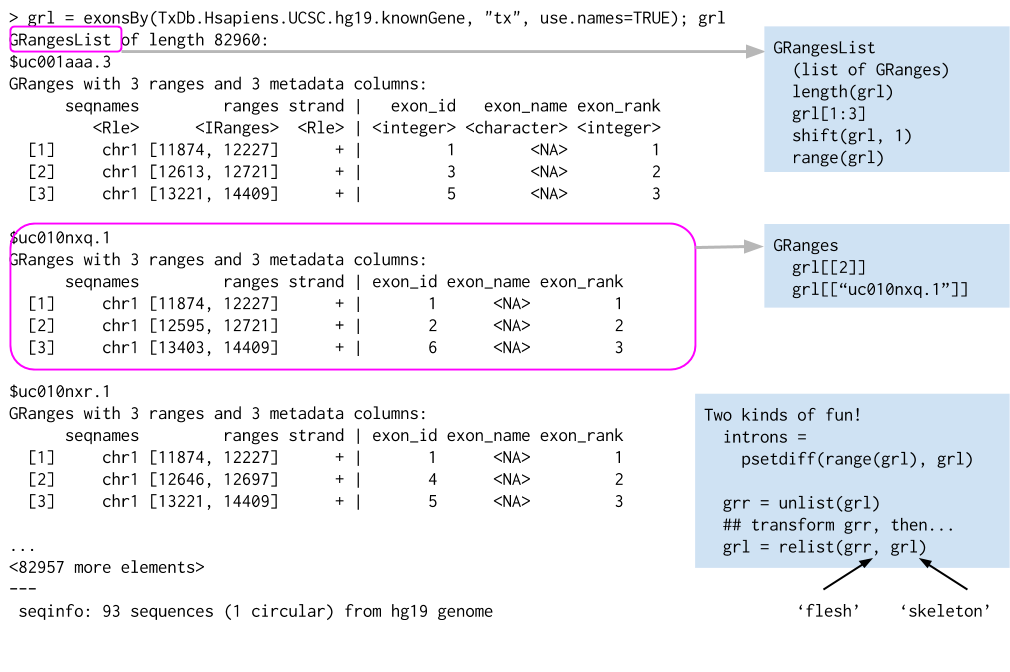 - e.g., exons-within-transcripts, alignments-within-reads
- e.g., exons-within-transcripts, alignments-within-reads